Teasamorelin
Potential treatment for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
Exploration of cognitive function improvement in aging populations
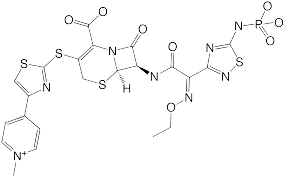
Tesamorelin is a synthetic analogue of growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH) designed to stimulate the pituitary gland to produce endogenous growth hormone (GH). It is primarily used to reduce excess abdominal fat in HIV-infected patients with lipodystrophy.
Mechanism of action
Tesamorelin binds to GHRH receptors in the anterior pituitary, stimulating the release of GH. This increase in GH leads to elevated levels of insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1), promoting lipolysis and reducing visceral adipose tissue. The compound’s structural modifications enhance its stability and resistance to enzymatic degradation, prolonging its activity.
Notable Studies
A 26-week randomized controlled trial demonstrated that tesamorelin significantly reduced visceral fat in HIV-infected patients with lipodystrophy.
Long-term studies indicate sustained decreases in visceral adipose tissue and triglyceride levels over 52 weeks without worsening glucose tolerance.
Risk Associated
Common side effects include injection site reactions (e.g., redness, pain, swelling), muscle aches, and nausea. Serious adverse effects may involve hypersensitivity reactions and increased risk of glucose intolerance. Tesamorelin is contraindicated in pregnancy and in patients with disrupted hypothalamic-pituitary axis.
Dosage
The recommended dosage is 2 mg administered subcutaneously once daily. Consistent daily administration is necessary to maintain therapeutic effects.
External link

Teasamorelin
Potential treatment for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
Exploration of cognitive function improvement in aging populations
Mechanism of action
Tesamorelin binds to GHRH receptors in the anterior pituitary, stimulating the release of GH. This increase in GH leads to elevated levels of insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1), promoting lipolysis and reducing visceral adipose tissue. The compound’s structural modifications enhance its stability and resistance to enzymatic degradation, prolonging its activity.
Risk
Associated
Common side effects include injection site reactions (e.g., redness, pain, swelling), muscle aches, and nausea. Serious adverse effects may involve hypersensitivity reactions and increased risk of glucose intolerance. Tesamorelin is contraindicated in pregnancy and in patients with disrupted hypothalamic-pituitary axis.
Notable Studies
A 26-week randomized controlled trial demonstrated that tesamorelin significantly reduced visceral fat in HIV-infected patients with lipodystrophy.
Long-term studies indicate sustained decreases in visceral adipose tissue and triglyceride levels over 52 weeks without worsening glucose tolerance.
Dosage
The recommended dosage is 2 mg administered subcutaneously once daily. Consistent daily administration is necessary to maintain therapeutic effects.
External link
Teasamorelin
Potential treatment for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
Exploration of cognitive function improvement in aging populations
Mechanism of action
Tesamorelin binds to GHRH receptors in the anterior pituitary, stimulating the release of GH. This increase in GH leads to elevated levels of insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1), promoting lipolysis and reducing visceral adipose tissue. The compound’s structural modifications enhance its stability and resistance to enzymatic degradation, prolonging its activity.

Risk
Associated
Common side effects include injection site reactions (e.g., redness, pain, swelling), muscle aches, and nausea. Serious adverse effects may involve hypersensitivity reactions and increased risk of glucose intolerance. Tesamorelin is contraindicated in pregnancy and in patients with disrupted hypothalamic-pituitary axis.
Notable Studies
A 26-week randomized controlled trial demonstrated that tesamorelin significantly reduced visceral fat in HIV-infected patients with lipodystrophy.
Long-term studies indicate sustained decreases in visceral adipose tissue and triglyceride levels over 52 weeks without worsening glucose tolerance.
Dosage
The recommended dosage is 2 mg administered subcutaneously once daily. Consistent daily administration is necessary to maintain therapeutic effects.
External link
-
Tesamorelin: Uses, Interactions, Mechanism of Action – DrugBank
-
Tesamorelin: Uses, Dosage, Side Effects, Warnings – Drugs.com
-
Effect of Tesamorelin on Visceral Fat and Liver Fat in HIV-Infected Patients – JAMA
-
Long-term safety and effects of tesamorelin, a growth hormone-releasing factor analogue – PubMed
-
Tesamorelin (subcutaneous route) – Mayo Clinic