Liraglutide
Chronic weight management
Cardiovascular risk reduction
Potential neuroprotective effects
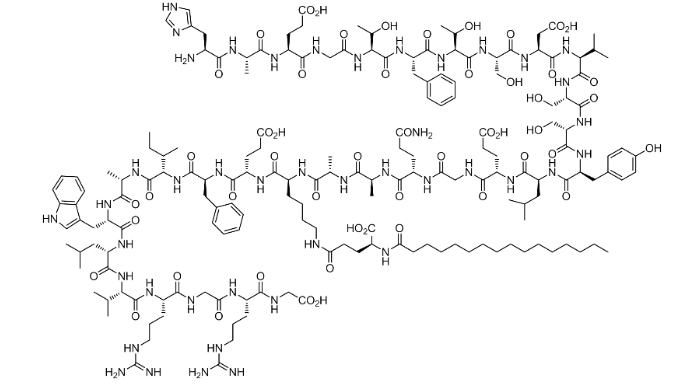
Liraglutide is a synthetic glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist used for managing type 2 diabetes and chronic obesity. It mimics the action of the natural incretin hormone GLP-1, enhancing insulin secretion and promoting weight loss.
Mechanism of action
Liraglutide binds to GLP-1 receptors, stimulating insulin release and inhibiting glucagon secretion in a glucose-dependent manner. It slows gastric emptying and increases satiety, leading to reduced food intake. Its acylation allows for albumin binding, extending its half-life to approximately 13 hours.
Notable Studies
The LEADER trial demonstrated that Liraglutide reduces the risk of major cardiovascular events in type 2 diabetes patients.
The SCALE Obesity and Prediabetes trial showed significant weight loss in obese individuals treated with Liraglutide.
Risk Associated
Gastrointestinal issues: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea
Risk of pancreatitis
Potential thyroid C-cell tumors (observed in rodents)
Hypoglycemia when combined with other antidiabetic agents
Dosage
For type 2 diabetes (Victoza): Start at 0.6 mg daily, increasing to 1.2 mg or 1.8 mg as needed.
For obesity (Saxenda): Start at 0.6 mg daily, increasing weekly by 0.6 mg to a maximum of 3.0 mg daily.
External link

Liraglutide
Chronic weight management
Cardiovascular risk reduction
Potential neuroprotective effects
Mechanism of action
Liraglutide binds to GLP-1 receptors, stimulating insulin release and inhibiting glucagon secretion in a glucose-dependent manner. It slows gastric emptying and increases satiety, leading to reduced food intake. Its acylation allows for albumin binding, extending its half-life to approximately 13 hours.
Risk
Associated
Gastrointestinal issues: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea
Risk of pancreatitis
Potential thyroid C-cell tumors (observed in rodents)
Hypoglycemia when combined with other antidiabetic agents
Notable Studies
The LEADER trial demonstrated that Liraglutide reduces the risk of major cardiovascular events in type 2 diabetes patients.
The SCALE Obesity and Prediabetes trial showed significant weight loss in obese individuals treated with Liraglutide.
Dosage
For type 2 diabetes (Victoza): Start at 0.6 mg daily, increasing to 1.2 mg or 1.8 mg as needed.
For obesity (Saxenda): Start at 0.6 mg daily, increasing weekly by 0.6 mg to a maximum of 3.0 mg daily.
External link
Liraglutide
Chronic weight management
Cardiovascular risk reduction
Potential neuroprotective effects
Mechanism of action
Liraglutide binds to GLP-1 receptors, stimulating insulin release and inhibiting glucagon secretion in a glucose-dependent manner. It slows gastric emptying and increases satiety, leading to reduced food intake. Its acylation allows for albumin binding, extending its half-life to approximately 13 hours.

Risk
Associated
Gastrointestinal issues: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea
Risk of pancreatitis
Potential thyroid C-cell tumors (observed in rodents)
Hypoglycemia when combined with other antidiabetic agents
Notable Studies
The LEADER trial demonstrated that Liraglutide reduces the risk of major cardiovascular events in type 2 diabetes patients.
The SCALE Obesity and Prediabetes trial showed significant weight loss in obese individuals treated with Liraglutide.
Dosage
For type 2 diabetes (Victoza): Start at 0.6 mg daily, increasing to 1.2 mg or 1.8 mg as needed.
For obesity (Saxenda): Start at 0.6 mg daily, increasing weekly by 0.6 mg to a maximum of 3.0 mg daily.
External link
-
StatPearls – Liraglutide Overview
-
DrugBank – Liraglutide Details
-
Drugs.com – Liraglutide Information
-
NCBI – Liraglutide for Weight Management
-
Wikipedia – Liraglutide